Cardiovascular System
The cardiovascular system consists of three components:
The function of the cardiovascular system is to transport oxygen and nutrients around the body to the cells that need it. At the same time it also removes carbon dioxide and other waste products from the body.
Components of Blood
The body contains approximately 5 litres of blood and this is a mixture made up of red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets all suspended in a liquid called plasma.

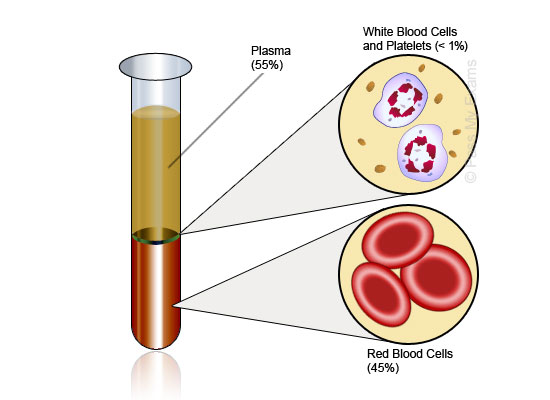
The table below provides more details on each of the separate components of blood.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Make up 40-50% of the total blood volume
- Made in the bone marrow
|
 |
| Function |
- Carry oxygen from lungs to all cells of the body
- Carry carbon dioxide away from cells
|
| Properties |
- Contain oxygen carrying molecule called haemoglobin which combines with oxygen to give oxyhaemoglobin.
Haemoglobin + Oxygen => Oxyhaemoglobin
- Haemoglobin also responsible for the red colour of blood
- Biconcave shape providing a large surface area to volume ratio to absorb the maximum amount of oxygen.
- Have no nucleus, therefore more surface area to carry haemoglobin and hence oxygen
- Small and flexible so can pass easily through blood vessels
|
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Make up 1% of the blood volume
- Made in the bone marrow
- Form part of the immune system
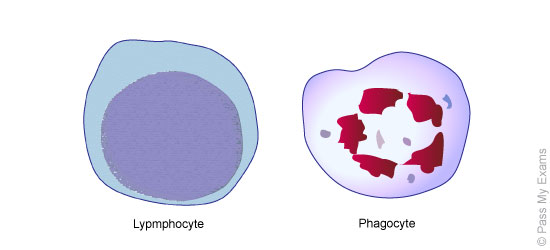
- Two main types: Lymphocytes and Phagocytes
|
 |
| Function |
- Defend the body against infection and disease
- Lypmhocytes: Recognise virus or bacteria as being foreign and make antibodies to attack and destroy them
- Phagocytes: Destroy virus and bacteria by engulfing them in a process known as phagocytosis. They take the germ into the cell then digest and destroy it.
|
| Properties |
- Have a large nucleus
- Larger than red blood cells
- Shape varies depending on which type of cell
- Have a flexible shape so that they can engulf microorganisms
|
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Fragments of larger cells
- Made in the bone marrow
|
 |
| Function |
- Help blood to clot by clumping together and forming a plug. (Therefore you do not bleed to death if you cut yourself).
- Protect the body by stopping bleeding
|
| Properties |
|
Plasma
- Makes up 55% of the blood volume
|
| Function |
- Transports dissolved substances e.g. Carbon dioxide, glucose, salts, urea, hormones, antibodies, plasma proteins around the body
- Brings nourishment to cells and removes waste products
- Prevents blood vessels from collapsing
|
| Properties |
- Yellow liquid part of the blood in which red and white blood cells as well as platelets are suspended
- 95% of it consists of water with many substances dissolved in it
|





