Percentages
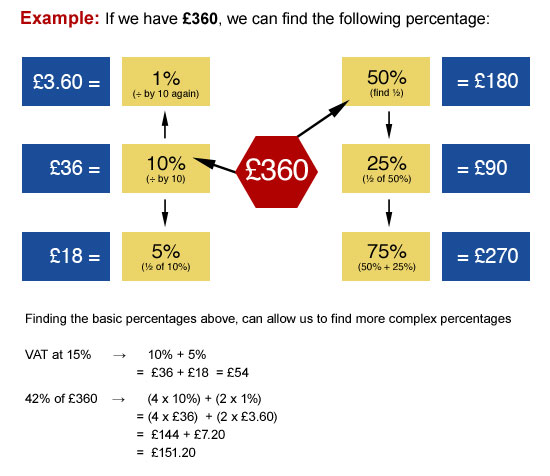
It is important to be able to find simple percentages of a quantity. In order to make these calculations you mainly need to be able to divide by 10 and halve numbers.
The Multiplier
The multiplier is the single decimal value used to multiply the amount you are working with.
For the £360 example
If we want to make 75% of £360 we can convert the 75% into a MULTIPLIER.
75% = 75/100 = 0.75
Therefore 75% of £360 = 0.75 x £360 = £270
This multiplier method is vital for calculating REVERSE PERCENTAGES, so you must make sure you understand this concept.
Increasing a quantity using the Multiplier
If we increase a 70kg sack of rubble by 20%, the end result would be the original 70kg plus an extra 20%.
Thus the original 70kg = 100%
 |
Increasing this by 20%, give us... |  |
To calculate the end value of our sack of rubble:
ORIGINAL + INCREASE = MULTIPLIER 100% + 20% = 120% Multiplier = 120% = 120/100 = 1.20 Increase in rubble = 1.20 x 70 = 84kg |
Further Examples
1. A salary of £22,000 increases by 5%, what is the new salary?
ORIGINAL + INCREASE = MULTIPLIER 100% + 5% = 105% Multiplier = 105% = 105/100 = 1.05 New salary = 1.05 x £22,000 = £23,100 |
2. A bottle of 125ml tomato ketchup has 35% extra in it, what is the new volume?
ORIGINAL + INCREASE = MULTIPLIER 100% + 35% = 135% Multiplier = 135% = 135/100 = 1.35 New volume = 1.35 x 125 = 168.75ml |
Decreasing a quantity using the Multiplier
When decreasing, we start with the original 100% and SUBTRACT the percentage.
Examples
1. A jacket costing £60 is reduced by 25% in a sale. What is the sale price of the jacket?
REMEMBER: The jacket is reduced, therefore we subtract from 100%
ORIGINAL - REDUCTION = MULTIPLIER 100% - 25% = 75% Multiplier = 75% = 75/100 = 0.75 Sale price = 0.75 x £60 = £45 |
2. A car depreciates by 15% per year. If the car cost £12,000 how much will it be worth by the end of the first year?
NOTE: Depreciation is the value that is LOST from an item; therefore we always SUBTRACT this percentage.
ORIGINAL - REDUCTION = MULTIPLIER 100% - 15% = 85% Multiplier = 85% = 85/100 = 0.85 Sale price = 0.85 x £12,000 = £10,200 |
Reading the question carefully
When attempting percentage questions, look carefully at what is being asked. Is the FINAL VALUE required or the INCREASE/DECREASE of the amount?
Example 1
A laptop cost £340 + 15% VAT. How much is the VAT?
Method 1: £340 => 10% = £34 |
Method 2: Laptop + VAT = 100% + 15% = 115% |
Example 2
A house cost £235,000 but lost 45% of its value in one year. How much did it lose?
Method 1: |
|
| £235,000 => so, Therefore, |
10% = £23,500 40% = £94,000 (23,500 x 4) 5% = £11,750 (23,500 ÷ 2) 45% = £105,750 |
Method 2: |
|
| 100% + 45% = 55% Multiplier = 55/100 = 0.55 Multiplier x House Cost = Current Value House Cost – Current Value = Value Lost £235,000 - £129,250= £105,750 |
|
Reverse Percentages
This method follows on from the multiplier method, but this time we DIVIDE by the multiplier.
The most common mistake for this method is when students do not read the question carefully and do not establish whether the question is asking for the ORIGINAL value or the NEW value.
Example 1
A dress is reduced by 20% in the January sale and now costs £180. What was the price of the dress in December?
| Step 1: | |||||||||||
| Establish the type of question first. This is a reverse percentage question as it requires the original value of the dress before the sale. | |||||||||||
| Step 2: | |||||||||||
Establish the multiplier. A 20% reduction in the sale means the multiplier used was: 100% - 20% = 80% Previously, we would have worked out the sale price as follows:
In this question the unknown quantity is the Original Price. Let the original price = x
Solving the equation for x, |
|||||||||||
Example 2
My sofa costs £2,350 with VAT. What is the price before VAT to the nearest penny?
| Step 1: | ||||||
| This is a reverse percentage question because the original value is required. | ||||||
| Step 2: | ||||||
The multiplier is 1.15 (100% + 15%) Let the original price = x
Solving the equation for x, |
||||||
